Have you had your vitamin D level tested lately? After a long winter spent indoors, we suggest you come see us!
One of the most common prescriptions we write at Enhanced Medical Care is for high dose ergocalciferol, which is the scientific name for vitamin D-2. This isn’t surprising considering that some studies have shown that as many as 75% of Americans have insufficient levels of this essential nutrient. Despite its name, vitamin D is not actually a vitamin, it’s a hormone precursor. Vitamin D supplements come in two forms: ergocalciferol (D-3), which occurs naturally in animal sources, and cholecalciferol (D-2), which can be derived from plants. These two molecules differ in how the kidneys and liver break them down into vitamin D’s biologically active form, calcitriol. Studies have shown them both to be effective in treating vitamin D deficiency. Calcitriol acts as a hormone and has regulatory functions. It helps with calcium absorption and regulation, has anti-inflammatory functions, and strengthens the neuromuscular and immune systems. It can come from several sources.
Vitamin D is present in dairy products, fatty fish (such as salmon, tuna, and swordfish), eggs, and also in many fortified foods, including orange juice and breakfast cereals. In the presence of UVB rays it can be synthesized from cholesterols in the skin, which is why it is often called the sunshine vitamin. Living at higher latitudes, like New England, reduces our sun exposure, especially in the approaching winter months, and puts us at increased risk for deficiency. Indeed, both of these sources do not provide very much vitamin D, which is why supplementation is often necessary.
Vitamin D is most well known for its role in bone health, and indeed it is essential to musculoskeletal function and maintenance. In fact vitamin D does much more for our bones, especially as we age, than most people realize. It facilitates calcium absorption in the intestines and regulates the levels of calcium in the blood, which is then sent to the bones for growth and repair, preventing osteoporosis. Studies have shown a 20% reduction in fractures in adults who supplement their vitamin D at appropriate doses. Vitamin D regulated calcium levels in the blood are also essential to the electrical impulses which govern muscle function; every time you take a step, blink, or open a book millions of calcium ions rush into, then out of, your muscle cells creating electric potentials. Calcium also mediates the contraction and extension the muscle fibers which move in response to these electrical signals. Adequate levels of vitamin D are associated with increased muscle strength, and studies have shown a 19% decrease in the risk of falls, which put your bones at risk.
Your heart, the most important muscle in your body, can also benefit from vitamin D supplementation. A study of 50,000 men showed a two times higher risk of heart attack in vitamin D deficient individuals. Other studies have shown inadequate vitamin D levels to be associated with higher risk of stroke, cardiovascular disease, and sudden cardiac death. Though the exact mechanisms behind these protective properties of vitamin D have yet to be determined, in addition to supporting muscular function, it is believed that vitamin D may help regulate blood pressure and thus prevent damage to your heart and arteries.
There are also epidemiologic as well as laboratory studies that support the hypothesis that adequate levels of vitamin D could decrease the risk of developing some types of cancer. So far the most evidence exists supporting this theory in regards to colorectal cancer, but there is also emerging science involving prostate and breast cancers. Vitamin D increases anti inflammatory cytokines and prevents pro inflammatory cytokines which can alter gene expression, slowing the spread of the cancer and promoting the death of these malignant cells.
Another area currently under intense study is the relationship between vitamin D and immune function and disorders. Several observational studies have found associations between adequate levels of vitamin D and being at decreased risk for autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis and type-1 diabetes. Other studies have shown a correlation between vitamin D supplementation and boosts in your body’s defenses against influenza, the common cold, and even tuberculosis. Vitamin D helps protect some white bloods cells, one of your body’s primary defense systems, from inflammation, and also help boost the production of antimicrobial proteins by these same white blood cells. More studies, however, are still needed to verify these findings; correlation does not indicate causation.
Daily vitamin D intake recommendations vary according to age and gender, but at our practice we advise our patients to maintain vitamin D blood serum levels between 40 and 90 ng/mL. Natural sources, such as sunlight (within healthy limits) and nutritious foods, are always the best sources of vitamin D. It is important to get your vitamin D levels checked regularly. For many people it is difficult to reach these daily recommendations or to maintain adequate levels of vitamin D in the blood, and in these cases supplementation may be helpful to achieve optimal wellness. Please do not hesitate to contact us if you have any questions about this, or any other, health issue.
To your health!
For more information, check out this great infographic from NaturalNews.com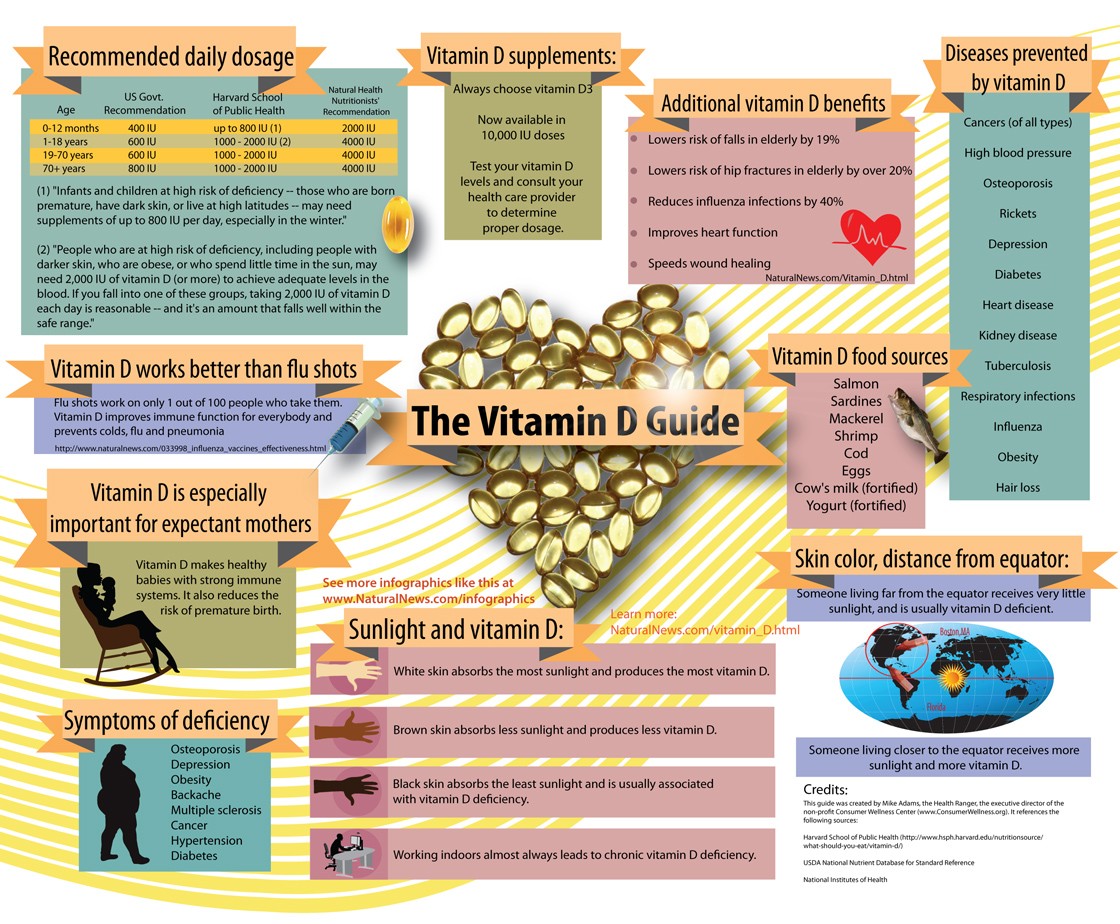







Leave A Comment